What is Call Forking?
Call forking enables incoming SIP calls to multiple endpoints simultaneously. That helps an organization when someone in the migration phase wants to take an incoming call on their preferred endpoint.
In this example, we take the inbound PSTN calls to AudioCodes SBC and fork the calls with Cisco Phones.
High-level architecture design -
Note: -I assume you already have Teams Direct Routing is implemented
Configure Dial Plan: -
Dial Plans let you categorize incoming calls (source or destination) based on source or
destination number. The device categorizes them by searching in the Dial Plan for rules that
match these numbers according to prefix, suffix, or whole number. The categorization result in
the Dial Plan is a tag corresponding to the matched rule.
You can assign a Dial Plan to an IP Group. After Classification and Inbound
Manipulation, the device checks if a Dial Plan is associated with the incoming call. It first
checks the source IP Group and if no Dial Plan is assigned, it checks the SRD. If a Dial Plan is
assigned to the IP Group or SRD, the device first searches the Dial Plan for a dial plan rule
that matches the source number and then it searches the Dial Plan for a rule that matches
the destination number. If matching dial plan rules are found, the tags configured for these
rules are used in the routing or manipulation processes as source or destination tags.
Dial Plan Rules -
Here I'm using "Call_Forking" as a tag.
IP Group -
Set Dial Plan - Teams_Call_Fork
Tag - "Call_Forking"
1 - Create IP to IP Routing Table for the primary route (e.g MS Teams).
IP to IP Routing Table -
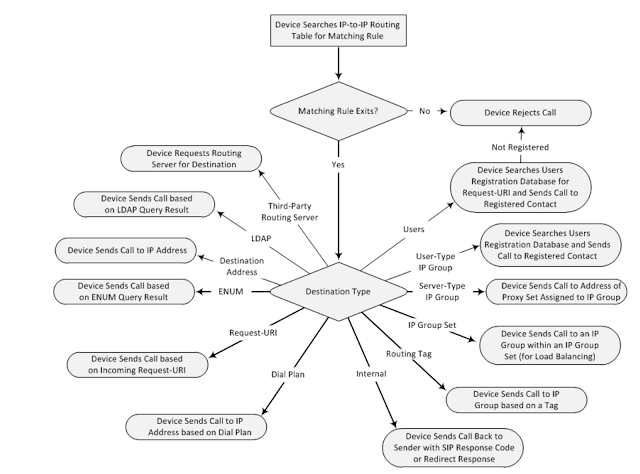
The device searches the table from top to bottom for the first rule that matches the
characteristics of the incoming call. If it finds a matching rule, it sends the call to the destination
configured for that rule. If it doesn't find a matching rule, it rejects the call.
IP-to-IP routing rules include two areas:
Match: Defines the characteristics of the incoming SIP dialog message (e.g., IP Group from
which the message is received).
Action: Defines the action done if the incoming call matches the characteristics of
the rule (i.e., routes the call to the specified destination).
Below routing table gives a summarized view of the destination types,
1 - Create IP to IP Routing Table for the primary route (e.g MS Teams).
- Alternative Route Options - Group Members Ignore Inputs - Route Row
- Set Destination Tag - Call_Forking
- Destination IP Group - MS Teams.
- Group Policy - Forking.
2- Create a Secondary (e.g Cisco) route right below the primary route, update the below attributes,
- Alternative Route Options - Group Members Ignore Inputs
- Destination Tag - Call_Forking
- Destination IP Group - Cisco
- Group Policy - Sequential






No comments:
Post a Comment